Neuroscience

 Zyprexa has rightfully received some bad press lately (so has Seroquel, but that story is more colorful). Although olanzapine is quite effective in treating schizophrenia and bipolar mania, it is notorious for causing very large weight gains in those taking it ("you'll gain five pounds just by filling the prescription" or 1.5 pounds per month according to a recent meta-analysis by Parsons et al., 2009). A 1999 article by Allison et al. was even worse: a gain of nearly a pound per week for 10 weeks (4.45 kg total!).1 One mechanism for this might involve increases in ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite (see Brain Health Hacks).
Zyprexa has rightfully received some bad press lately (so has Seroquel, but that story is more colorful). Although olanzapine is quite effective in treating schizophrenia and bipolar mania, it is notorious for causing very large weight gains in those taking it ("you'll gain five pounds just by filling the prescription" or 1.5 pounds per month according to a recent meta-analysis by Parsons et al., 2009). A 1999 article by Allison et al. was even worse: a gain of nearly a pound per week for 10 weeks (4.45 kg total!).1 One mechanism for this might involve increases in ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite (see Brain Health Hacks).
 Enter modafinil, which has been touted as a cognitive enhancing drug taken by some shifty academics. A recent paper on the Effects of Modafinil on Dopamine and Dopamine Transporters in the Male Human Brain (Volkow et al., 2009) caused some to ask whether modafinil might be addictive. But the answer is that it's probably not, even though it increases the level of dopamine (the "reward" neurotransmitter) by blocking the dopamine transporter. In addition to its effects on dopamine, modafinil also affects the norepinephrine neurotransmitter system, as shown in a technically difficult neuroimaging study (Minzenberg et al., 2008) of the human locus coeruleus, a small nucleus in the brainstem. Also on the plus side for modafinil is its potential usefulness in psychiatric practice: for improving attention and executive control function in schizophrenia (Morein-Zamir et al., 2007), and as an add-on medication in treating bipolar depression (Belmaker, 2007).
Enter modafinil, which has been touted as a cognitive enhancing drug taken by some shifty academics. A recent paper on the Effects of Modafinil on Dopamine and Dopamine Transporters in the Male Human Brain (Volkow et al., 2009) caused some to ask whether modafinil might be addictive. But the answer is that it's probably not, even though it increases the level of dopamine (the "reward" neurotransmitter) by blocking the dopamine transporter. In addition to its effects on dopamine, modafinil also affects the norepinephrine neurotransmitter system, as shown in a technically difficult neuroimaging study (Minzenberg et al., 2008) of the human locus coeruleus, a small nucleus in the brainstem. Also on the plus side for modafinil is its potential usefulness in psychiatric practice: for improving attention and executive control function in schizophrenia (Morein-Zamir et al., 2007), and as an add-on medication in treating bipolar depression (Belmaker, 2007).
But the paper of today (Roerig et al., 2009) did none of that, instead enrolling healthy control participants2 and seeing whether modafinil attenuated the olanzapine-induced weight gain. A previous experiment by this group (Roerig et al., 2005) observed a 5 lb. increase over a 2 week period, significantly greater than both risperadone and placebo (Table 2). The number of calories consumed was numerically greater, but did not reach significance.
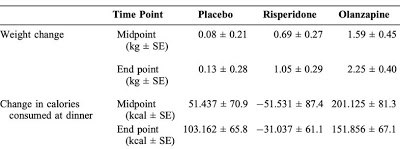
Table 2 (Roerig et al., 2005). Weight Change (in kilograms). Calorie Change (in kilocalories).
What about the current study?
Footnote
1 I happened to notice that both of those studies had strong ties to Pfizer... coincidentally [or not], Pfizer touts its own atypical drug (Geodon) as not causing weight gain.
2 Who wants to take olanzapine for fun and profit? Anyone? In addition to getting fat, "You'll sleep 10-16 hours a day. You won't care about anything."
References
Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC, Weiden PJ. (1999). Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 156:1686-96.
Belmaker RH. (2007). Modafinil add-on in the treatment of bipolar depression. Am J Psychiatry 164:1143-5.
Minzenberg MJ, Watrous AJ, Yoon JH, Ursu S, Carter CS. (2008). Modafinil shifts human locus coeruleus to low-tonic, high-phasic activity during functional MRI. Science 322:1700-2.
Morein-Zamir S, Turner DC, Sahakian BJ. (2007). A review of the effects of modafinil on cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 33:1298-306.
Parsons B, Allison DB, Loebel A, Williams K, Giller E, Romano S, Siu C. (2009). Weight effects associated with antipsychotics: A comprehensive database analysis. Schizophr Res. Mar 23. [Epub ahead of print].
Roerig JL, Mitchell JE, de Zwaan M, Crosby RD, Gosnell BA, Steffen KJ, Wonderlich SA. (2005). A comparison of the effects of olanzapine and risperidone versus placebo on eating behaviors. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 25(5):413-8.

Roerig, J., Steffen, K., Mitchell, J., Crosby, R., & Gosnell, B. (2009). An Exploration of the Effect of Modafinil on Olanzapine Associated Weight Gain in Normal Human Subjects Biological Psychiatry, 65 (7), 607-613 DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.037
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F, Wang GJ, Jayne M, Hooker JM, Wong C, Hubbard B, Carter P, Warner D, King P, Shea C, Xu Y, Muench L, Apelskog-Torres K. (2009). Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA 301:1148-54.
Note: The sound begins after 8 sec, and then... FEED YOUR HEAD!
- Glutamate Agonist Ly2140023: A New Treatment For Schizophrenia?
High hopes for new schizophrenia drugs Drug trial hailed as first major breakthrough for 50 years. By Alison Abbott . . . The side effects of LY2140023, including insomnia and emotional instability, are slightly different to those of olanzapine although...
- Alzheimer Disease: Dimebon Results
A press release from earlier today by Pfizer: Pfizer And Medivation Announce Results From Two Phase 3 Studies In Dimebon (latrepirdine) Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Development Program [snip] "About the CONNECTION Study "CONNECTION is a Phase 3, multi-national,...
- Risperdal (risperidone) And Pediatric Schizophrenia And Bipolar Disorder
An FDA press release from yesterday: FDA Approves Risperdal for Two Psychiatric Conditions in Children and Adolescents The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Risperdal (risperidone) for the treatment of schizophrenia in adolescents, ages...
- Neuropsychology Abstract Of The Day: Modafinil And Fatigue In Depression
Lam JY, Freeman MK, & Gates ME. Modafinil augmentation for residual symptoms of fatigue in patients with a partial response to antidepressants. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Jun;41(6):1005-12. Epub 2007 May 22. University of Alabama Health System-Birmingham,...
- Modafinil, Adhd, And The Fda
From The Washington Post: Use of Drug to Treat ADHD in Children Opposed Associated Press Friday, March 24, 2006; Page A11 The narcolepsy drug modafinil should not be approved as a treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children until...
Neuroscience
One pill makes you larger and one pill makes you small

And the ones that mother gives you
Don't do anything at all
Go ask Alice
When she's ten feet tall
White Rabbit
---Jefferson Airplane
No, we're not really discussing hallucinogenic drugs today (despite the psychedelic reference). The real question for today is this: Does the wakefulness drug modafinil (Provigil) lessen the weight gain caused by atypical antipsychotics? Not really (Roerig et al., 2009), despite what the Elsevier press release tells us:Don't do anything at all
Go ask Alice
When she's ten feet tall
White Rabbit
---Jefferson Airplane
Combating Weight Gain Caused by Antipsychotic TreatmentsPhiladelphia, PA, March 26, 2009 – Antipsychotic drugs, such as olanzapine (Zyprexa), risperidone (Risperdal), and quetiapine (Seroquel) are commonly used to treat psychotic disorders like schizophrenia, but also bipolar disorder and even behavioral problems related to dementia. Unfortunately, the weight gain commonly experienced with antipsychotic treatment is an important side effect for many patients, and causes many patients to discontinue their use leading to even further problems. Biological Psychiatry, in its April 1st issue, is now publishing a new study that has evaluated an add-on treatment to potentially reduce treatment-associated weight gain.In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Dr. James Roerig and colleagues evaluated the effect of modafinil on olanzapine-associated weight gain in normal volunteer subjects. Modafinil is a drug currently used to increase wakefulness in individuals with sleep disorders, such as narcolepsy. All of the subjects received olanzapine, and half also received modafinil treatment while the other half instead received placebo. After three weeks, although the body mass index was increased in both groups, those receiving olanzapine/placebo showed significantly greater weight increase than those receiving olanzapine/modafinil.The April 1st issue, hmm... You'll notice the study was conducted in normal volunteer participants and only for a 3 week period. What you didn't see in the press release is that during the 3 week period, 10 of the 50 original subjects withdrew from the trial (2 in modafinil + olanzapine group, and 8 in placebo + olanzapine group).
 Zyprexa has rightfully received some bad press lately (so has Seroquel, but that story is more colorful). Although olanzapine is quite effective in treating schizophrenia and bipolar mania, it is notorious for causing very large weight gains in those taking it ("you'll gain five pounds just by filling the prescription" or 1.5 pounds per month according to a recent meta-analysis by Parsons et al., 2009). A 1999 article by Allison et al. was even worse: a gain of nearly a pound per week for 10 weeks (4.45 kg total!).1 One mechanism for this might involve increases in ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite (see Brain Health Hacks).
Zyprexa has rightfully received some bad press lately (so has Seroquel, but that story is more colorful). Although olanzapine is quite effective in treating schizophrenia and bipolar mania, it is notorious for causing very large weight gains in those taking it ("you'll gain five pounds just by filling the prescription" or 1.5 pounds per month according to a recent meta-analysis by Parsons et al., 2009). A 1999 article by Allison et al. was even worse: a gain of nearly a pound per week for 10 weeks (4.45 kg total!).1 One mechanism for this might involve increases in ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite (see Brain Health Hacks). Enter modafinil, which has been touted as a cognitive enhancing drug taken by some shifty academics. A recent paper on the Effects of Modafinil on Dopamine and Dopamine Transporters in the Male Human Brain (Volkow et al., 2009) caused some to ask whether modafinil might be addictive. But the answer is that it's probably not, even though it increases the level of dopamine (the "reward" neurotransmitter) by blocking the dopamine transporter. In addition to its effects on dopamine, modafinil also affects the norepinephrine neurotransmitter system, as shown in a technically difficult neuroimaging study (Minzenberg et al., 2008) of the human locus coeruleus, a small nucleus in the brainstem. Also on the plus side for modafinil is its potential usefulness in psychiatric practice: for improving attention and executive control function in schizophrenia (Morein-Zamir et al., 2007), and as an add-on medication in treating bipolar depression (Belmaker, 2007).
Enter modafinil, which has been touted as a cognitive enhancing drug taken by some shifty academics. A recent paper on the Effects of Modafinil on Dopamine and Dopamine Transporters in the Male Human Brain (Volkow et al., 2009) caused some to ask whether modafinil might be addictive. But the answer is that it's probably not, even though it increases the level of dopamine (the "reward" neurotransmitter) by blocking the dopamine transporter. In addition to its effects on dopamine, modafinil also affects the norepinephrine neurotransmitter system, as shown in a technically difficult neuroimaging study (Minzenberg et al., 2008) of the human locus coeruleus, a small nucleus in the brainstem. Also on the plus side for modafinil is its potential usefulness in psychiatric practice: for improving attention and executive control function in schizophrenia (Morein-Zamir et al., 2007), and as an add-on medication in treating bipolar depression (Belmaker, 2007).But the paper of today (Roerig et al., 2009) did none of that, instead enrolling healthy control participants2 and seeing whether modafinil attenuated the olanzapine-induced weight gain. A previous experiment by this group (Roerig et al., 2005) observed a 5 lb. increase over a 2 week period, significantly greater than both risperadone and placebo (Table 2). The number of calories consumed was numerically greater, but did not reach significance.

Table 2 (Roerig et al., 2005). Weight Change (in kilograms). Calorie Change (in kilocalories).
What about the current study?
In the completer analysis, the primary outcome variable, BMI [body mass index] change from baseline, was significantly different between groups with the olanzapine/placebo group experiencing a greater increase in BMI than the olanzapine/modafinil group (.89 + .59 vs. .47 + .50 kg/m2, p<.05). The mean weight gain in the placebo group was approximately twice that seen in the modafinil group (2.67 + 1.79 vs. 1.33 + 1.41 kg) over the 3-week exposure, and this approached significance.HOWEVER, when controlled for gender [there were 8 men in the placebo group and zero in the modafinil group - nice!], the BMI difference was significant for week 1 but not for weeks 2 and 3. Over the short term of this study, there were no major differences in calories consumed, glucose and lipid levels, sleep, food cravings, or hunger and satiety ratings (with the exception of a slight increase in morning hunger for the placebo group). Ultimately, the authors concluded that...
The results of this trial should not be extrapolated to clinical practice at this time. These data do serve to support further evaluation in a patient population to determine if the weight modifying effect of modafinil can be demonstrated over a longer period of time.Obviously, the people who receive prescriptions for this class of medications will be taking them for longer than 3 weeks, and the detrimental metabolic effects accumulate over months and years. Anything that can counteract the increased risks of significant weight gain, diabetes, hyperglycemia, and metabolic syndrome will be helpful in preserving the health of those who take atypical antipsychotics.
Footnote
1 I happened to notice that both of those studies had strong ties to Pfizer... coincidentally [or not], Pfizer touts its own atypical drug (Geodon) as not causing weight gain.
2 Who wants to take olanzapine for fun and profit? Anyone? In addition to getting fat, "You'll sleep 10-16 hours a day. You won't care about anything."
References
Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC, Weiden PJ. (1999). Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 156:1686-96.
Belmaker RH. (2007). Modafinil add-on in the treatment of bipolar depression. Am J Psychiatry 164:1143-5.
Minzenberg MJ, Watrous AJ, Yoon JH, Ursu S, Carter CS. (2008). Modafinil shifts human locus coeruleus to low-tonic, high-phasic activity during functional MRI. Science 322:1700-2.
Morein-Zamir S, Turner DC, Sahakian BJ. (2007). A review of the effects of modafinil on cognition in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 33:1298-306.
Parsons B, Allison DB, Loebel A, Williams K, Giller E, Romano S, Siu C. (2009). Weight effects associated with antipsychotics: A comprehensive database analysis. Schizophr Res. Mar 23. [Epub ahead of print].
Roerig JL, Mitchell JE, de Zwaan M, Crosby RD, Gosnell BA, Steffen KJ, Wonderlich SA. (2005). A comparison of the effects of olanzapine and risperidone versus placebo on eating behaviors. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 25(5):413-8.

Roerig, J., Steffen, K., Mitchell, J., Crosby, R., & Gosnell, B. (2009). An Exploration of the Effect of Modafinil on Olanzapine Associated Weight Gain in Normal Human Subjects Biological Psychiatry, 65 (7), 607-613 DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2008.10.037
Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Logan J, Alexoff D, Zhu W, Telang F, Wang GJ, Jayne M, Hooker JM, Wong C, Hubbard B, Carter P, Warner D, King P, Shea C, Xu Y, Muench L, Apelskog-Torres K. (2009). Effects of modafinil on dopamine and dopamine transporters in the male human brain: clinical implications. JAMA 301:1148-54.
Note: The sound begins after 8 sec, and then... FEED YOUR HEAD!
- Glutamate Agonist Ly2140023: A New Treatment For Schizophrenia?
High hopes for new schizophrenia drugs Drug trial hailed as first major breakthrough for 50 years. By Alison Abbott . . . The side effects of LY2140023, including insomnia and emotional instability, are slightly different to those of olanzapine although...
- Alzheimer Disease: Dimebon Results
A press release from earlier today by Pfizer: Pfizer And Medivation Announce Results From Two Phase 3 Studies In Dimebon (latrepirdine) Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Development Program [snip] "About the CONNECTION Study "CONNECTION is a Phase 3, multi-national,...
- Risperdal (risperidone) And Pediatric Schizophrenia And Bipolar Disorder
An FDA press release from yesterday: FDA Approves Risperdal for Two Psychiatric Conditions in Children and Adolescents The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Risperdal (risperidone) for the treatment of schizophrenia in adolescents, ages...
- Neuropsychology Abstract Of The Day: Modafinil And Fatigue In Depression
Lam JY, Freeman MK, & Gates ME. Modafinil augmentation for residual symptoms of fatigue in patients with a partial response to antidepressants. Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 2007 Jun;41(6):1005-12. Epub 2007 May 22. University of Alabama Health System-Birmingham,...
- Modafinil, Adhd, And The Fda
From The Washington Post: Use of Drug to Treat ADHD in Children Opposed Associated Press Friday, March 24, 2006; Page A11 The narcolepsy drug modafinil should not be approved as a treatment for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder in children until...
