Neuroscience

In light of all the sensationalistic press coverage about a journal article that wasn't publicly available last week, it's worth taking a moment to look at the actual experiment. Of course, the savvy skeptics know by now that the paper in question (Immordino-Yang et al., 2009) has absolutely nothing to do with Twitter (see Recommended Reading below for a recap). Instead, the authors conducted a neuroimaging study to examine the brain's response to stories designed to elicit the emotions of admiration and compassion. To do this, the participants (n=13) first watched a series of mini-documentary narratives about real people (who were not celebrities). Each of the 50 narratives was 60-90 sec long, and incorporated audio, video, and still images to convey stories categorized as:
The comparisons of interest were pain (compassion) vs. non-pain (admiration), and emotional responses to other peoples’ social/psychological conditions (AV, CSP) vs. to their physical conditions (AS, CPP). One of the first issues discussed is the recruitment of homeostatic mechanisms when experiencing these social emotions:
Other components in the somatic marker circuit include the insular cortex, a region implicated in interoceptive awareness of bodily states (Craig, 2009), and somatosensory cortices responsive to external stimuli. Because activity in the anterior insula features primarily in the Twitter-warped distortion of the story, I'll start here with the authors' third hypothesis:
Let's start with a simpler example. The figure below shows the averaged hemodynamic response function (HRF) in the primary visual cortex to a series of flashes. The HRF peaks at ~5 sec after the flash, whereas neurons in primary visual cortex fire within 50 msec and drop off shortly thereafter. Thus, the hemodynamic response to even a simple sensory stimulus lags behind neuronal firing by 5 sec.
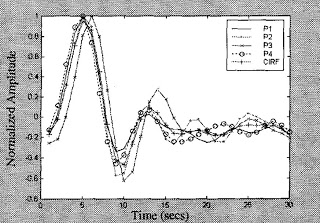
Fig. 2 (Calhoun et al., 1998). Time courses from four regions in the calcarine cortex (Pl-P4) and the averaged response (CIRQ). Amplitude units are normalized to a maximum of one and a baseline of zero.
The next example shows the HRFs in occipital regions and the insula while subjects viewed rotating objects. The precise details aren't important here, but note the peak latency for the HRF in the insula is around 6-8 sec, with the later peak for novel objects (compared to repeated objects).
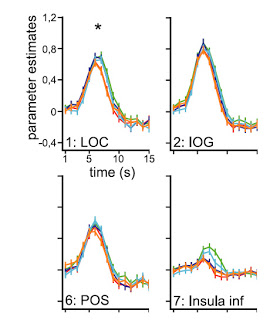
Fig 2C (Weigelt et al., 2007). Event-related deconvolved BOLD fMRI responses (GLM parameter estimates averaged across trials and subjects for all voxels in each ROI) reported against time for each of the experimental conditions.
That brings us back to Immordino-Yang et al. and the emotional narratives. In the figure below, note that the HRF time course does peak earlier for the CPP condition compared to the others, as predicted. However, the CSP condition rises at the same time, albeit with a later (very broad) peak.
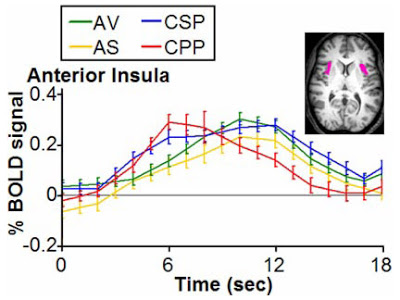
Fig. 3 (Immordino-Yang et al., 2009). Event-related averages for the time courses of admiration and compassion in the anterior insula, with standard errors. Units are percentage change in BOLD signal and time in seconds; time courses are not corrected for hemodynamic delay. For display purposes, BOLD data have been linearly interpolated to 1-s resolution. The volume of interest is displayed in pink. Conditions: AV (green): admiration for virtue; AS (yellow): admiration for skill; CSP (blue): compassion for social pain; CPP (red): compassion for physical pain. Note the rapid rise and dissipation of CPP versus the slower and more sustained rise of CSP, AV, and AS.
It's critical to note that the onset of a felt emotion is not as easy to determine as the onset of a visual object. Although more detailed methods are in the Supplementary Materials not available as of this writing, it seems that respiration and heart rate data were obtained in 7 of the 13 subjects to help with this. I would say these psychophysiological responses, in concert with the participants' own reaction times for rating their subjective responses, would provide a more accurate measure of how long it takes to feel an emotion than the fMRI data. It's hard to know what an insular HRF of 6 sec vs. 10 sec means when watching a fast-paced movie or reading the CNN news crawl or yes, spending too much time on Twitter. Nonetheless, on the basis of these imprecise latency measures, the authors speculate:

I'll leave you with this final thought: where's the line between admiration and envy, between compassion and schadenfreude? There actually is a recent paper on the Neural Correlates of Envy and Schadenfreude (Takahashi et al., 2009), and for now I'll refer you to this nice summary in Pure Pedantry.
ADDENDUM (Monday 4:20 PM): You can read more details about the Methods in the Supporting Information, which is now freely available to all on the PNAS website, as is the open access article itself.
Recommended Twitter Reading:
Social media threats hyped by science reporting, not science (Ars Technica)Experts say new scientific evidence helpfully justifies massive pre-existing moral prejudice. (Bad Science)For the last time: that "Twitter is Evil" paper is not about Twitter! (Bioephemera)Is Twitter evil? (Cosmic Log at MSNBC - despite the ridiculous headline, it's one of the few popular science articles to talk about the actual study... it even included a figure from the paper)
The Neurology of Twitter (The Neurocritic proposes an actual fMRI study of Twitter, complete with predicted results)
The Neurology of Twitter, Part 2 (Yet another recap of the media circus, with a time line of certain events)
References
Craig AD. How do you feel--now? The anterior insula and human awareness. (2009). Nat Rev Neurosci. 10:59-70.
Damasio AR. (1996). The somatic marker hypothesis and the possible functions of the prefrontal cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 351:1413-20.

Mary Helen Immordino-Yang, Andrea McColl, Hanna Damasio, and Antonio Damasio. (2009). Neural correlates of admiration and compassion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

- Envy Is A Stronger Motivator Than Admiration
Admiration is happy self-surrender; envy is unhappy self-assertion. Søren KierkegaardMind Hacks, Not Exactly Rocket Science, The Frontal Cortex ... there are so many successful blogs out there for the Digest to admire. Or envy. In fact envy might be...
- Harry Potter And The Prisoner Of Mid-cingulate Cortex
What happens in the brain during a highly immersive reading experience? According to the fiction feeling hypothesis (Jacobs, 2014), narratives with highly emotional content cause a deeper sense of immersion by engaging the affective empathy network to...
- The Neurology Of Twitter
It was bound to happen. Some neuroimaging lab will conduct an actual fMRI experiment to examine the so-called "Neural Correlates of Twitter" -- so why not write a preemptive blog post to report on the predicted results from such a study, before anyone...
- I Can't Feel Anything...
...and I can't describe it, either. from Jackson, Meltzoff, & Decety (2005) The Neurocritic has just noticed a new neuroimaging paper on empathy in individuals with alexithimia, which is an inability to describe one's own feelings. Coincidentally,...
- I Wanna Hold Your Hand
This one was widely covered in the popular press a few weeks ago, albeit the Psychological Science article itself has yet to appear in print (or in cyberspace). From the New York Times: Holding Loved One's Hand Can Calm Jittery Neurons Married women...
Neuroscience
Neural Correlates of Admiration and Compassion and Envy and Schadenfreude

In light of all the sensationalistic press coverage about a journal article that wasn't publicly available last week, it's worth taking a moment to look at the actual experiment. Of course, the savvy skeptics know by now that the paper in question (Immordino-Yang et al., 2009) has absolutely nothing to do with Twitter (see Recommended Reading below for a recap). Instead, the authors conducted a neuroimaging study to examine the brain's response to stories designed to elicit the emotions of admiration and compassion. To do this, the participants (n=13) first watched a series of mini-documentary narratives about real people (who were not celebrities). Each of the 50 narratives was 60-90 sec long, and incorporated audio, video, and still images to convey stories categorized as:
1. Admiration for virtue (AV), which involved people performing highly virtuous, morally admirable acts. The narratives emphasized the virtuous and morally admirable nature of the protagonist, such as dedication to an important cause despite difficult obstacles, and did not include displays of notable skill.2. Admiration for skill (AS), which involved people adeptly performing rare and difficult feats, e.g., an athletic or musical performance, with both physical and cognitive components. No physically or socially painful acts were shown, and the skillful feats, although amazing, did not imply a virtuous protagonist or reveal a virtuous act.3. Compassion for social pain (CSP), which involved people in states of grief, despair, social rejection, or other difficult psychological circumstances. No physical pain was evident in these narratives, and the troubling circumstances were discerned from the descriptions, rather than being apparent in the images shown.4. Compassion for physical pain (CPP), which involved people sustaining a physical injury. The injuries were caused by sports and other mishaps and had no moral or social implications. The injuries were not the result of malevolence, and the participants were reassured that the injuries had no long-term implications....5. Control narratives, which involved comparable living, mentally competent people engaged in or discussing how they felt about typical activities under commonplace social circumstances. These circumstances were engaging but not emotion provoking.After each of the narratives, the subjects were asked to discuss how they felt about the protagonist's situation. This part of the study took 2 hrs, and was conducted outside the scanner. For the fMRI portion of the protocol, 5 sec recaps of all 50 scenarios were presented, and the task was to:
induce in themselves for each story, as strongly as possible, a similar emotional state to the one they had experienced during the preparation session and to push a button to indicate the strength of the emotion they achieved in the scanner (from 1 to 4...). Participants were asked to report candidly on the strength of their current feelings in the scanner, rather than on the strength of feeling they remembered from the preparation session.OK, so the subjects were first asked to remember how they felt 2 hrs ago, then try to duplicate that feeling, and then report on how they feel now (rather than before). So there's a memory component and a decision component (i.e., to not confuse past feelings with the present). Each trial was sorted post hoc on the strength of the reported emotion, and only the effective trials were included in the analysis.
The comparisons of interest were pain (compassion) vs. non-pain (admiration), and emotional responses to other peoples’ social/psychological conditions (AV, CSP) vs. to their physical conditions (AS, CPP). One of the first issues discussed is the recruitment of homeostatic mechanisms when experiencing these social emotions:
It is well known that basic emotions such as fear, sadness, and happiness and limited social emotions such as moral indignation engage neural systems concerned with sensing and regulating body function with varying patterns, and it has been hypothesized that among those systems, the insula plays an especially prominent role. It is also known that engagement of social emotions and the consequent feeling for another’s social/psychological situation are described by poets and lay people alike in visceral and bodily terms and in terms of their heightening effect on one’s own self-awareness or consciousness.Basically, people may have visceral responses to the circumstances of others. How do these responses differ across physical vs. psychological situations? For example, admiring a gymnast's skill on the balance beam vs. admiring a student's charity work with Habitat for Humanity? Or feeling compassion for a single mother who loses her job vs. feeling compassion for one who sprains her ankle? Although it's not mentioned in the paper, this idea draws on Antonio Damasio's somatic marker hypothesis (e.g., Damasio, 1996). Perhaps this omission occurred because two of the main regions implicated -- the ventromedial prefrontal cortex (VMPFC) and the amygdala -- were not discussed in the paper [however VMPFC is difficult to image using fMRI because of susceptibility artifacts]. The somatic marker hypothesis is succinctly described by the title of one of Damasio's books: The Feeling of What Happens: Body and Emotion in the Making of Consciousness (1999).
Other components in the somatic marker circuit include the insular cortex, a region implicated in interoceptive awareness of bodily states (Craig, 2009), and somatosensory cortices responsive to external stimuli. Because activity in the anterior insula features primarily in the Twitter-warped distortion of the story, I'll start here with the authors' third hypothesis:
3. that activation in the anterior insula would peak and dissipate more quickly for CPP than for CSP or varieties of admiration.In a way, this is a trivial prediction, because one can evaluate the sprained ankle narrative more quickly than the job loss scenario. In fact, I will argue below that simple behavioral response time might be a more precise measure of how long it takes to generate the emotion in question than is the hemodynamic response (blood flow changes, measured by the BOLD signal in fMRI) in the insular cortex. One reason for this is because of the significant delay (5-6 sec at least) between initial neural firing and the peak of the hemodynamic response, which is estimated using a procedure that is not trivial for something as complex as an emotional response (for a more detailed discussion of this issue, I recommend this PPT file from Jodi Culham's excellent fMRI 4 Newbies site).
Let's start with a simpler example. The figure below shows the averaged hemodynamic response function (HRF) in the primary visual cortex to a series of flashes. The HRF peaks at ~5 sec after the flash, whereas neurons in primary visual cortex fire within 50 msec and drop off shortly thereafter. Thus, the hemodynamic response to even a simple sensory stimulus lags behind neuronal firing by 5 sec.

Fig. 2 (Calhoun et al., 1998). Time courses from four regions in the calcarine cortex (Pl-P4) and the averaged response (CIRQ). Amplitude units are normalized to a maximum of one and a baseline of zero.
The next example shows the HRFs in occipital regions and the insula while subjects viewed rotating objects. The precise details aren't important here, but note the peak latency for the HRF in the insula is around 6-8 sec, with the later peak for novel objects (compared to repeated objects).

Fig 2C (Weigelt et al., 2007). Event-related deconvolved BOLD fMRI responses (GLM parameter estimates averaged across trials and subjects for all voxels in each ROI) reported against time for each of the experimental conditions.
That brings us back to Immordino-Yang et al. and the emotional narratives. In the figure below, note that the HRF time course does peak earlier for the CPP condition compared to the others, as predicted. However, the CSP condition rises at the same time, albeit with a later (very broad) peak.

Fig. 3 (Immordino-Yang et al., 2009). Event-related averages for the time courses of admiration and compassion in the anterior insula, with standard errors. Units are percentage change in BOLD signal and time in seconds; time courses are not corrected for hemodynamic delay. For display purposes, BOLD data have been linearly interpolated to 1-s resolution. The volume of interest is displayed in pink. Conditions: AV (green): admiration for virtue; AS (yellow): admiration for skill; CSP (blue): compassion for social pain; CPP (red): compassion for physical pain. Note the rapid rise and dissipation of CPP versus the slower and more sustained rise of CSP, AV, and AS.
It's critical to note that the onset of a felt emotion is not as easy to determine as the onset of a visual object. Although more detailed methods are in the Supplementary Materials not available as of this writing, it seems that respiration and heart rate data were obtained in 7 of the 13 subjects to help with this. I would say these psychophysiological responses, in concert with the participants' own reaction times for rating their subjective responses, would provide a more accurate measure of how long it takes to feel an emotion than the fMRI data. It's hard to know what an insular HRF of 6 sec vs. 10 sec means when watching a fast-paced movie or reading the CNN news crawl or yes, spending too much time on Twitter. Nonetheless, on the basis of these imprecise latency measures, the authors speculate:
If replicated, this finding could have important implications for the role of culture and education in the development and operation of social and moral systems; in order for emotions about the psychological situations of others to be induced and experienced, additional time may be needed for the introspective processing of culturally shaped social knowledge. The rapidity and parallel processing of attention-requiring information, which hallmark the digital age, might reduce the frequency of full experience of such emotions, with potentially negative consequences.And there's your "Twitter is evil" angle.

I'll leave you with this final thought: where's the line between admiration and envy, between compassion and schadenfreude? There actually is a recent paper on the Neural Correlates of Envy and Schadenfreude (Takahashi et al., 2009), and for now I'll refer you to this nice summary in Pure Pedantry.
ADDENDUM (Monday 4:20 PM): You can read more details about the Methods in the Supporting Information, which is now freely available to all on the PNAS website, as is the open access article itself.
Recommended Twitter Reading:
Social media threats hyped by science reporting, not science (Ars Technica)Experts say new scientific evidence helpfully justifies massive pre-existing moral prejudice. (Bad Science)For the last time: that "Twitter is Evil" paper is not about Twitter! (Bioephemera)Is Twitter evil? (Cosmic Log at MSNBC - despite the ridiculous headline, it's one of the few popular science articles to talk about the actual study... it even included a figure from the paper)
The Neurology of Twitter (The Neurocritic proposes an actual fMRI study of Twitter, complete with predicted results)
The Neurology of Twitter, Part 2 (Yet another recap of the media circus, with a time line of certain events)
References
Craig AD. How do you feel--now? The anterior insula and human awareness. (2009). Nat Rev Neurosci. 10:59-70.
Damasio AR. (1996). The somatic marker hypothesis and the possible functions of the prefrontal cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 351:1413-20.

Mary Helen Immordino-Yang, Andrea McColl, Hanna Damasio, and Antonio Damasio. (2009). Neural correlates of admiration and compassion. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

- Envy Is A Stronger Motivator Than Admiration
Admiration is happy self-surrender; envy is unhappy self-assertion. Søren KierkegaardMind Hacks, Not Exactly Rocket Science, The Frontal Cortex ... there are so many successful blogs out there for the Digest to admire. Or envy. In fact envy might be...
- Harry Potter And The Prisoner Of Mid-cingulate Cortex
What happens in the brain during a highly immersive reading experience? According to the fiction feeling hypothesis (Jacobs, 2014), narratives with highly emotional content cause a deeper sense of immersion by engaging the affective empathy network to...
- The Neurology Of Twitter
It was bound to happen. Some neuroimaging lab will conduct an actual fMRI experiment to examine the so-called "Neural Correlates of Twitter" -- so why not write a preemptive blog post to report on the predicted results from such a study, before anyone...
- I Can't Feel Anything...
...and I can't describe it, either. from Jackson, Meltzoff, & Decety (2005) The Neurocritic has just noticed a new neuroimaging paper on empathy in individuals with alexithimia, which is an inability to describe one's own feelings. Coincidentally,...
- I Wanna Hold Your Hand
This one was widely covered in the popular press a few weeks ago, albeit the Psychological Science article itself has yet to appear in print (or in cyberspace). From the New York Times: Holding Loved One's Hand Can Calm Jittery Neurons Married women...
